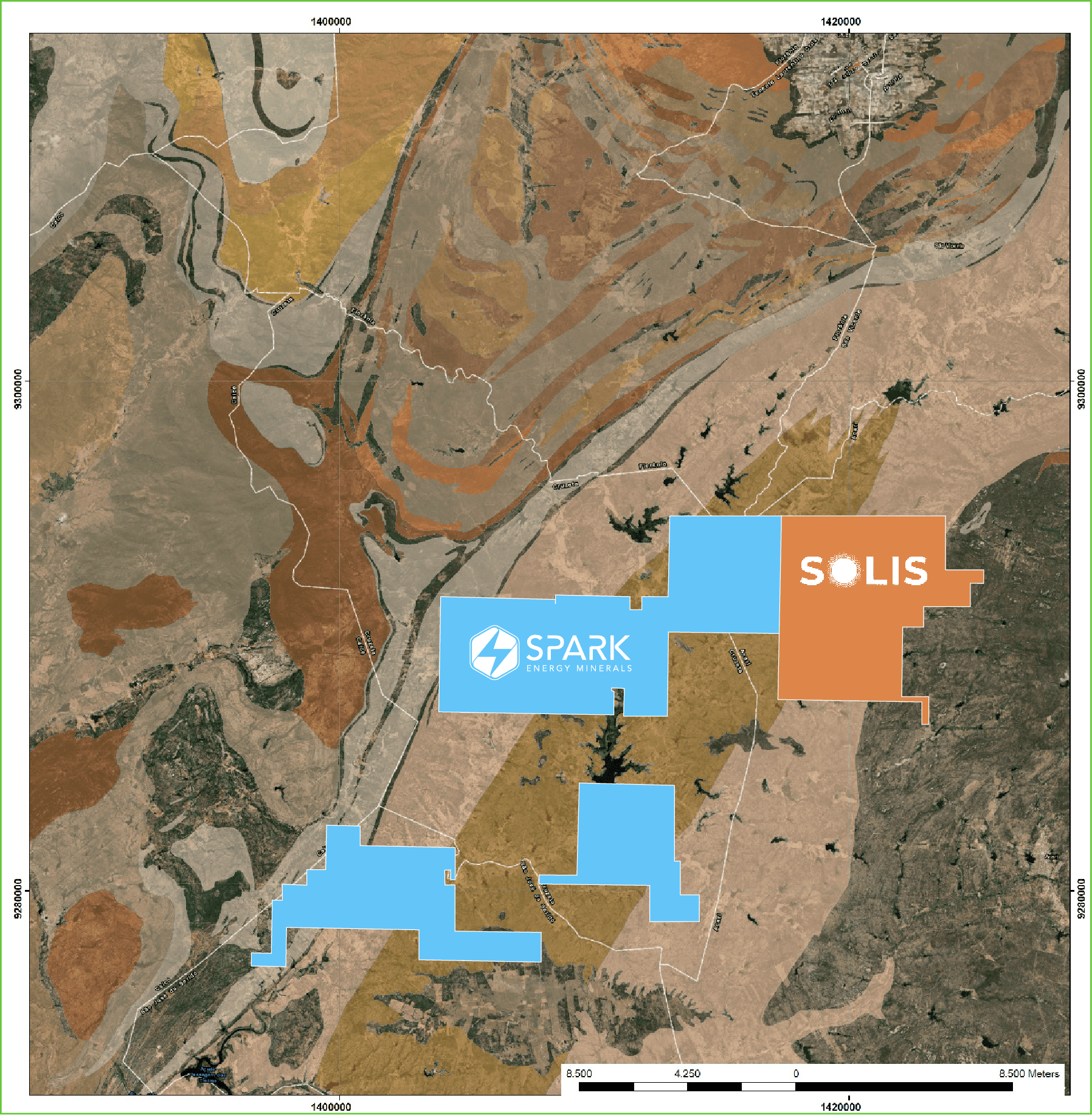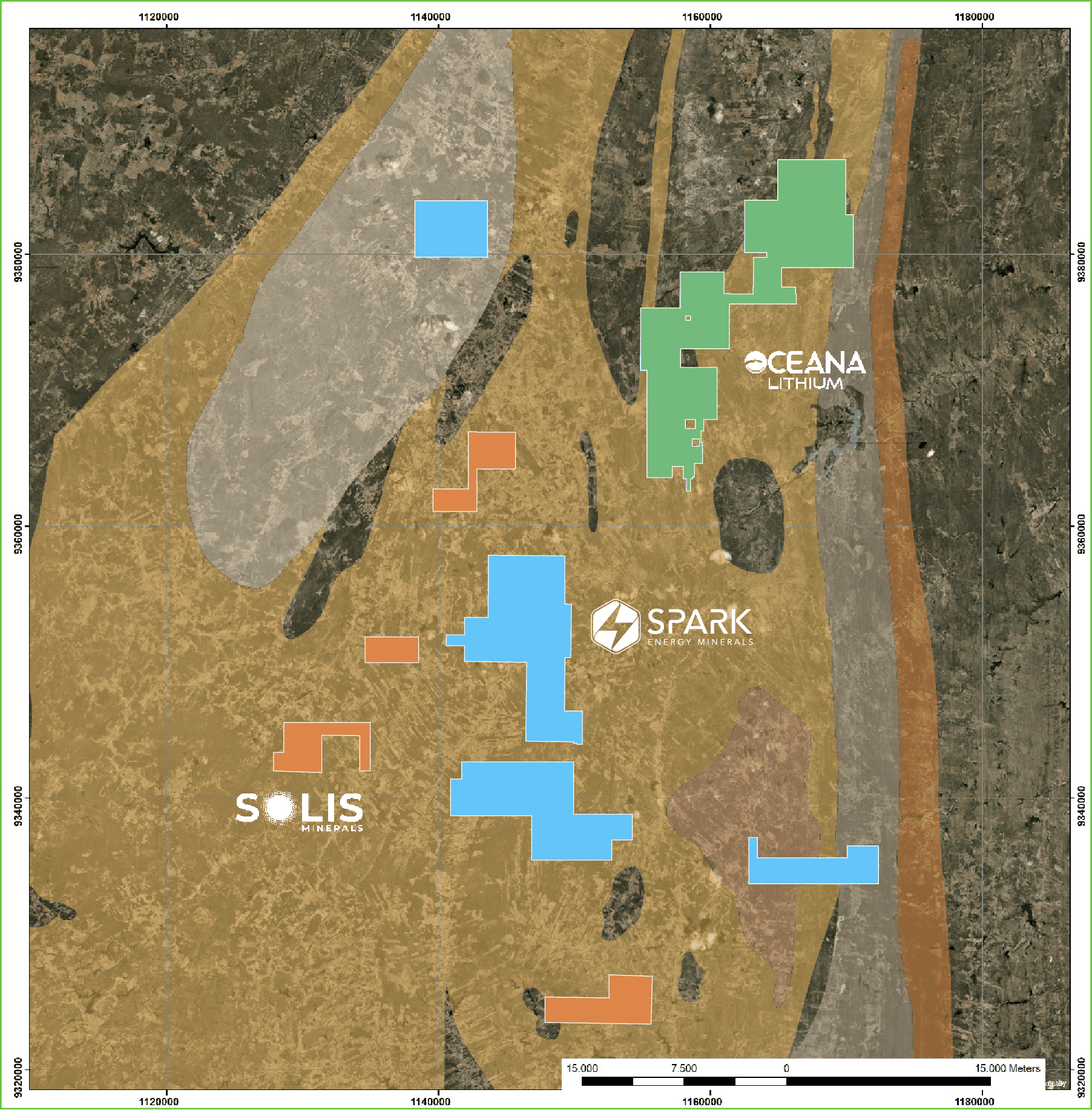
Largest Contiguous Tenement: Spark Energy controls the largest continuous land package in the region, spanning over 64,000 hectares in Brazil’s Lithium Valley.
Total Tenement Package: All of Spark’s tenements combined in the Lithium Valley span an impressive 91,900-hectares
Prospective Geology: Geophysical data suggests lithium-bearing pegmatites exposed in erosional
windows through regolith cover.
Untapped Potential: Presence of spodumene particles in heavy mineral concentrates panned from streams highlight the untapped potential on Spark’s property.
Strategic Location
The Right Host Rock
Spark’s Lithium and REE project covers an extensive area of 91,900-hectares combined spanning over 30km wide by 50km long. This is an exceptionally large contiguous exploration package located in the highly prospective “Lithium Valley” of Minas Gerais State, Brazil.
Four high-priority exploration targets Cruzeta, Grota do Maquém, Agua Branca, and Caladão were defined for immediate follow-up.
Next Steps for Exploration Include:
Detailed structural interpretation of the pegmatites throughout the tenements.
Continue systematic regional geological mapping and sampling over the remaining sections of the property that have yet to be explore.
Systematic stream sediment sampling across all permits and follow up with targeted Auger grid sampling. The project has significant soil cover > 1m and requires mechanised Auger to undertake effective geochemistry.
Once geochemical targets have been defined then drilling can be assessed to test the Lithium mineralization initially within Cruzeta, Grota do Maquém, and Agua Branca.
Undertake road-based Auger drilling campaign utilising existing road access at the Caladão REE target. The potential for extensive REE has been defined by ongoing stream and grab sampling along with publicly available information from peer explorers within the region.
Advanced Lithium Targets
Initial ground reconnaissance including geological mapping completed over the Caladão Granite.
Spark’s tenements are contiguous with Axel REE Limited’s Caladão Project and has returned high-grade REE and gallium mineralization after completing a first phase drill program.
Axel REE Limited’s drill results include 49.92m @ 5,909ppm TREO with 1m @ 22,115ppm TREO.
Initial soil and stream sediment samples collected by Spark include:
Anomalous TREO results > 3,000ppm in soils samples and;
Anomalous TREO results > 6,000ppm in stream sediment samples.
Geological Thesis